Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) 
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security system that requires more than one method of authentication from independent categories of credentials to verify the user’s identity for a login or other transaction.
This added layer of protection helps to ensure that the user is who they claim to be by requiring more than just a password.
MFA is an essential tool in the fight against unauthorised access and cyber threats, which is particularly crucial when accessing sensitive information or conducting online transactions.
How Does Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Work?
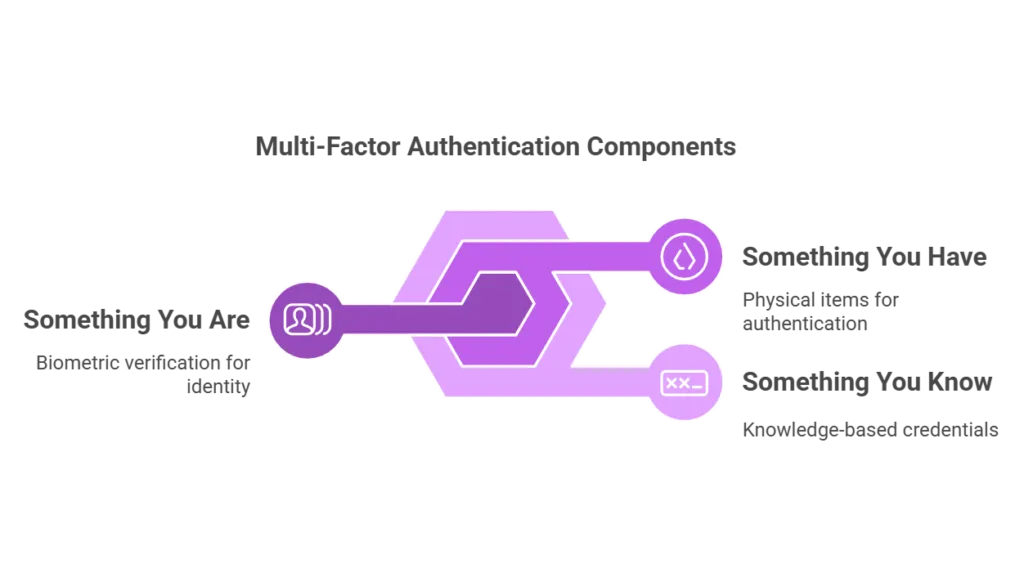
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) operates on the principle that the more independent factors used to verify a user’s identity, the greater the confidence that the user is who they claim to be. These factors typically fall into three categories:
- Something You Know: This includes passwords, PINs, or answers to secret questions.
- Something You Have: This could be a smartphone, a hardware token, or a smart card.
- Something You Are: This involves biometric verification such as fingerprints, retina scans, or voice recognition.
When a user attempts to access an account, they must provide two or more of these factors. For example, they might enter a password (something they know) and then provide a code sent to their smartphone (something they have).
Benefits of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) offers several significant benefits:
- Enhanced Security: By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA significantly reduces the chances of unauthorised access.
- Data Protection: It helps protect sensitive information from being accessed by malicious actors.
- Compliance: Many regulatory standards and laws require the use of MFA for protecting certain types of data.
- User Trust: Users feel more secure knowing their accounts have an extra layer of protection.
Types of Multi-Factor Authentication Methods
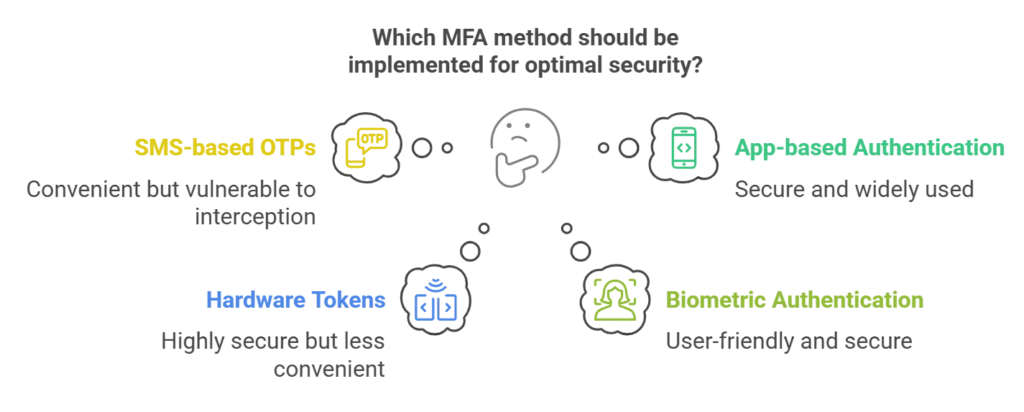
Several methods can be used in MFA, each providing varying levels of security:
- SMS-based OTPs (One-Time Passwords): A temporary code sent to the user’s phone via text message.
- App-based Authentication: Applications like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator generate time-based or event-based OTPs.
- Hardware Tokens: Physical devices that generate OTPs.
- Biometric Authentication: Uses physical characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice recognition.
- Push Notifications: Prompts sent to a user’s registered device, which they must approve to complete the authentication process.
By adding an extra layer of security, MFA helps protect sensitive data, comply with regulations, and build user trust.
Common Authenticator Apps
When it comes to enhancing the security of your online accounts, authenticator apps play a crucial role. These apps generate time-based one-time passcodes (TOTPs) that you use in addition to your password. Here are some of the most popular authenticator apps:
- Google Authenticator: This app is widely used and trusted for its simplicity and reliability. It generates TOTPs that refresh every 30 seconds. Google Authenticator is available for both Android and iOS devices and supports multiple accounts.
- Microsoft Authenticator: Ideal for users with Microsoft accounts, this app also supports other accounts. It offers additional features like passwordless sign-in and a built-in password manager. The app is available on Android and iOS.
- Authy: Known for its user-friendly interface, Authy provides backup options, making it easy to recover your tokens if you lose your device. It supports multiple devices and offers cloud synchronisation, ensuring you can access your codes from any device.
- LastPass Authenticator: This app integrates seamlessly with the LastPass password manager, providing an additional layer of security. It supports push notifications for easy authentication and is available on Android and iOS.
- 1Password: Besides being a robust password manager, 1Password also offers TOTP generation for multifactor authentication. It provides a secure and convenient way to manage both your passwords and authentication codes.
- 2FAS: An open-source authenticator app that prioritises privacy and security. 2FAS collects minimal data and includes extensions for popular browsers, making it a versatile choice for users who value transparency.
- Aegis Authenticator: Best suited for Android devices, Aegis Authenticator offers extensive customisation options and easy backup capabilities. It is open-source and focuses on providing a secure and user-friendly experience.
These authenticator apps help enhance the security of your online accounts by generating one-time passcodes that are required in addition to your password. By using any of these apps, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorised access to your accounts.
7 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using MFA
Multifactor authentication (MFA) significantly enhances the security of your online accounts, but it’s important to use it correctly. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using MFA:
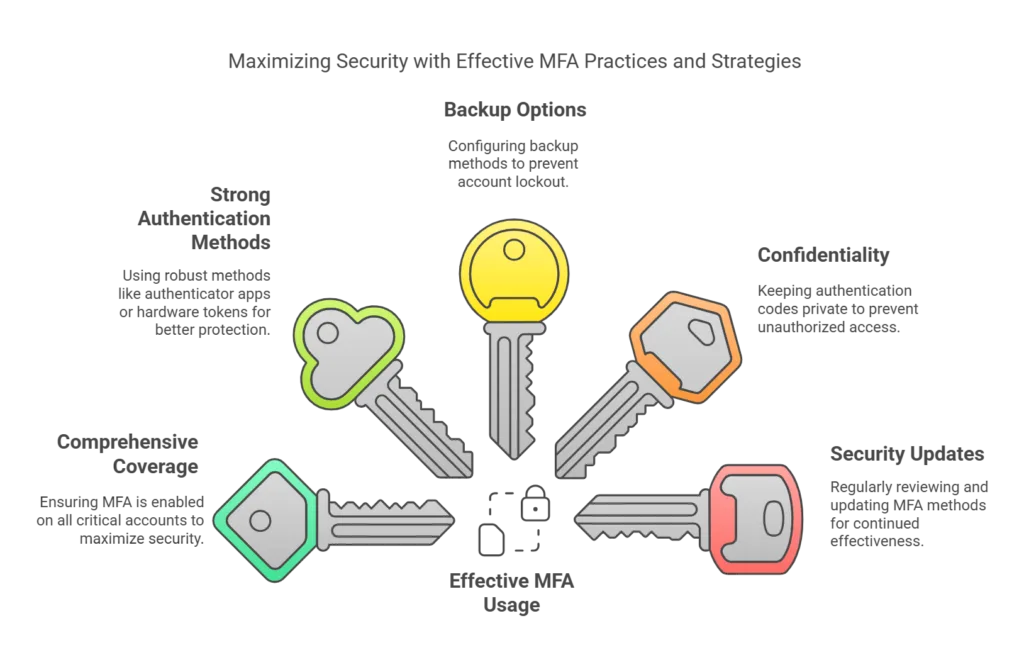
- Not Enabling MFA on All Accounts: Implementing MFA only on certain accounts or systems leaves other accounts vulnerable to attacks. Ensure MFA is enabled on all critical accounts to maximise security.
- Using Weak Authentication Factors: Relying on less secure methods like SMS or email-based authentication can be risky. Opt for stronger methods like authenticator apps or hardware tokens to provide better protection.
- Ignoring Backup Options: Failing to set up backup methods can lock you out of your accounts if you lose access to your primary MFA method. Always configure backup options like recovery codes or secondary devices to ensure you can regain access if needed.
- Sharing Authentication Codes: Never share your authentication codes with anyone. Treat them as confidential information to prevent unauthorized access to your accounts.
- Leaving Hardware Tokens Unattended: Physical tokens should be kept secure and not left unattended where they can be stolen or lost. Always store them in a safe place when not in use.
- Using Easily Guessed Answers for Security Questions: Avoid using easily guessed answers for security questions, as they can be exploited by attackers. Choose answers that are difficult to guess and not publicly available.
- Not Updating MFA Methods: Regularly review and update your MFA methods to ensure they remain secure and effective. This includes updating your authentication apps and devices as needed.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can enhance the security of your accounts and make the most of multifactor authentication.
Frequently Asked Questions About Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security measure that requires users to provide multiple forms of verification to access a system, application, or online account. Instead of relying solely on a password, MFA adds additional layers of security by combining two or more independent credentials: something the user knows (like a password), something the user has (like a smartphone), and something the user is (like a fingerprint). This multi-layered approach significantly enhances security by making it much more difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access, even if they have obtained the user's password.
Why is Multi-Factor Authentication important?
Multi-Factor Authentication is crucial because it greatly enhances security. Passwords alone can be easily compromised through phishing attacks, social engineering, or brute force attacks. By requiring additional forms of verification, MFA mitigates these risks. It ensures that even if a password is stolen, the attacker would still need access to the second or third factor to gain entry. This added complexity makes it much harder for cybercriminals to breach accounts, protecting sensitive information and reducing the likelihood of data breaches.
How does MFA differ from Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a subset of Multi-Factor Authentication. 2FA specifically requires two forms of authentication, typically a combination of something you know (password) and something you have (a code sent to your phone). MFA, on the other hand, can involve two or more factors and might include additional elements like biometrics (something you are). In essence, all 2FA is MFA, but not all MFA is limited to just two factors. MFA provides an even higher level of security by potentially incorporating multiple layers beyond just two factors.
What are some common methods used in MFA?
- SMS-based OTPs (One-Time Passwords): A temporary code sent to the user's phone via text message.
-App-based Authentication: Apps like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator generate time-based or event-based OTPs.
- Hardware Tokens: Physical devices, like USB tokens, that generate one-time codes.
- Biometric Authentication: Uses physical characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice recognition.
- Push Notifications: Prompts sent to a user's registered device, which they must approve to complete the authentication process. Each method has its strengths and provides varying levels of security and convenience.
Is MFA necessary for all online accounts?
Although MFA provides a strong security layer, no system is completely foolproof. Attackers can potentially bypass MFA through sophisticated methods such as SIM swapping, phishing for secondary authentication codes, or exploiting vulnerabilities in the authentication process. However, bypassing MFA typically requires significantly more effort and sophistication than compromising a single-factor authentication system. Users should remain vigilant and use best practices, like regularly updating security settings and being cautious of phishing attempts.
How do I set up MFA on my accounts?
Setting up MFA typically involves accessing the security settings of your account and enabling MFA. Here's a general process:
- Access Account Settings: Navigate to the security or privacy settings of the account.
- Enable MFA: Look for the option to enable or set up Multi-Factor Authentication.
- Choose Authentication Methods: Select your preferred methods, such as SMS, app-based authentication, or biometrics.
- Follow Setup Instructions: Follow the prompts to configure and activate your chosen methods.
- Save Backup Options: Ensure you set up backup authentication methods like backup codes or secondary email addresses to avoid lockout in case you lose access to your primary authentication method.
Does using MFA slow down the login process?
While MFA does add an additional step to the login process, the time delay is usually minimal. The extra verification step is a small trade-off for the significantly enhanced security it provides. Most users find the added time to be negligible compared to the peace of mind and protection against unauthorized access. Additionally, some methods, like biometric authentication, can be almost instantaneous.
What should I do if I lose access to my second factor (e.g., phone or hardware token)?
- Backup Codes: These are pre-generated codes that you can use if you lose access to your primary authentication method.
- Secondary Email or Phone Number: Some services allow you to set up a secondary email or phone number for recovery purposes.
- Security Questions: Answering predefined security questions to verify your identity. It is crucial to set up these backup options during the initial MFA setup to ensure you can regain access to your account if needed.
Are there any costs associated with using MFA?
Many MFA methods, such as SMS-based OTPs and app-based authentication, are free to use. However, certain advanced MFA options, like hardware tokens or premium authentication services, might involve costs. The investment in these additional security measures is often justified by the enhanced protection they provide, especially for accounts containing highly sensitive information.

Virgin Media Broadband Black Friday Deals with 3 Months Free Service
Virgin Media Unveils Generous Broadband Black Friday Deals with Three Months Free Service Consumers looking to make significant savings on their internet services this Black Friday are in for a treat. Virgin Media has launched an impressive offer, providing three months free on a selection of their broadband packages. This move positions the company as […]

